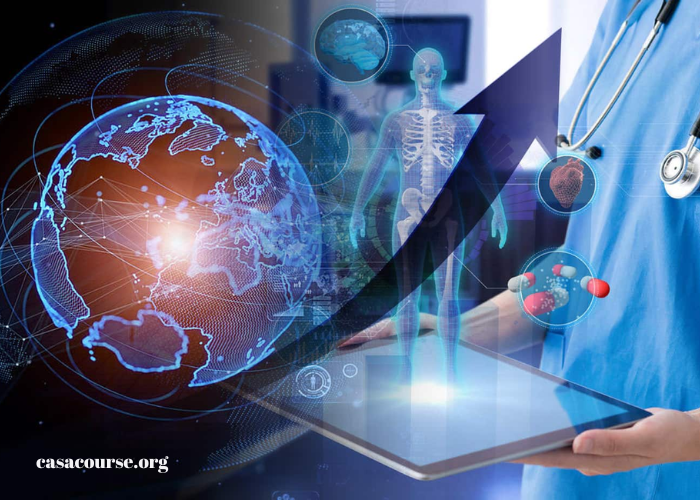
In the 21st century, the healthcare industry is undergoing a remarkable transformation, driven by the rapid advancement of technology. From artificial intelligence (AI) to blockchain, the convergence of healthcare and technology is revolutionizing how medical care is delivered, accessed, and managed. This article explores the current trends, future prospects, and potential challenges of tech-driven healthcare, and how these innovations are shaping the future of medical care.
The Rise of Tech-Driven Healthcare
The integration of technology into healthcare is not a new concept. However, the pace at which it is evolving and the extent of its impact on the industry is unprecedented. This surge in technological adoption is primarily fueled by the need to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and address the inefficiencies in the traditional healthcare system.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are at the forefront of tech-driven healthcare. These technologies are being leveraged to enhance diagnostics, personalize treatment plans, and streamline administrative processes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, imaging results, and genetic information, to identify patterns and predict outcomes with remarkable accuracy.
For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools can detect diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart conditions at an early stage, often before symptoms become apparent. This early detection allows for timely intervention, improving the chances of successful treatment and reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Machine learning, a subset of AI, is being used to develop predictive models that can anticipate patient needs, optimize resource allocation, and enhance decision-making. In personalized medicine, AI and ML are enabling the development of tailored treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history, leading to more effective and targeted therapies.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Telemedicine has emerged as a critical component of tech-driven healthcare, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. It has transformed how patients interact with healthcare providers, offering a convenient and accessible alternative to in-person visits. Through video consultations, patients can receive medical advice, prescriptions, and follow-up care without leaving their homes.
Remote monitoring technologies, such as wearable devices and mobile health apps, allow for continuous tracking of patients’ vital signs and health metrics. These tools enable healthcare providers to monitor patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, in real-time, facilitating early intervention and reducing hospital readmissions.
The integration of telemedicine and remote monitoring is particularly beneficial for rural and underserved populations, who may have limited access to healthcare facilities. By bridging the gap between patients and providers, these technologies are helping to ensure that quality healthcare is accessible to all, regardless of geographic location.
Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology, best known for its role in securing cryptocurrencies, is finding new applications in healthcare. Its decentralized and immutable nature makes it an ideal solution for managing and securing sensitive health data.
In healthcare, blockchain can be used to create secure, interoperable health records that can be accessed by authorized providers across different institutions. This not only enhances the accuracy and continuity of care but also reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Moreover, blockchain can streamline supply chain management in the pharmaceutical industry by providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of the journey of drugs from manufacturer to patient. This helps combat the issue of counterfeit drugs, ensuring that patients receive safe and authentic medications.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are revolutionizing various aspects of healthcare, from surgical procedures to logistics and patient care. Robotic-assisted surgeries, for example, allow for greater precision and control, reducing the risk of complications and shortening recovery times.
In addition to surgery, robots are being used in rehabilitation, elderly care, and even in hospital logistics. Automated systems can handle tasks such as medication dispensing, sterilization, and transportation of supplies, freeing up healthcare workers to focus on more complex and critical tasks.
Robotics is also playing a significant role in addressing the growing demand for healthcare services, particularly in aging populations. Assistive robots can help elderly patients with daily activities, monitor their health, and provide companionship, improving their quality of life and reducing the burden on caregivers.
Genomics and Precision Medicine
The field of genomics is rapidly advancing, thanks to technological innovations that allow for the sequencing and analysis of entire genomes at a fraction of the time and cost it once required. This has paved the way for precision medicine, an approach to healthcare that tailors treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient.
Precision medicine involves using genetic information, along with other data, to determine the most effective treatments for a particular patient. This approach is especially valuable in the treatment of cancer, where targeted therapies can be developed based on the genetic mutations driving the disease.
The potential of genomics extends beyond treatment to include prevention and early detection. By understanding an individual’s genetic predispositions, healthcare providers can develop personalized prevention strategies, such as lifestyle modifications or early screening programs, to reduce the risk of developing certain conditions.
Big Data and Analytics
The healthcare industry generates massive amounts of data, from patient records and clinical trials to medical imaging and wearable devices. Big data analytics is the process of analyzing and extracting insights from these large datasets to improve decision-making, enhance patient outcomes, and optimize operations.
In clinical settings, big data analytics can identify trends and patterns that may not be apparent through traditional methods. For example, by analyzing data from thousands of patients, healthcare providers can identify risk factors for diseases, predict outbreaks, and develop more effective treatment protocols.
Furthermore, big data is playing a crucial role in advancing research and development in healthcare. By analyzing data from clinical trials, researchers can identify potential drug candidates, understand disease mechanisms, and accelerate the development of new therapies.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the benefits of tech-driven healthcare are undeniable, the adoption of these technologies is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is data privacy and security. As healthcare becomes increasingly digital, the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches rises. Protecting patient data and ensuring compliance with regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), is essential.
Another challenge is the potential for technology to exacerbate existing disparities in healthcare. While telemedicine and remote monitoring have the potential to improve access to care, there is a risk that vulnerable populations, such as the elderly or those in low-income areas, may be left behind due to lack of access to digital tools or internet connectivity.
Ethical considerations also come into play with the use of AI and machine learning in healthcare. Questions around accountability, bias in algorithms, and the potential for AI to replace human judgment are important issues that need to be addressed as these technologies continue to evolve.
The Future of Tech-Driven Healthcare
The future of healthcare is undoubtedly tech-driven, with ongoing innovations poised to further transform the industry. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even greater integration of AI, robotics, genomics, and other cutting-edge technologies into medical practice.
One of the most exciting prospects is the potential for personalized medicine to become the norm rather than the exception. With advances in genomics and data analytics, treatments will become increasingly tailored to the individual, improving outcomes and reducing side effects.
Moreover, the continued development of telemedicine and remote monitoring will make healthcare more accessible and convenient for patients worldwide. As 5G networks and other communication technologies expand, the reach and capabilities of telehealth services will grow, bringing quality care to even the most remote corners of the globe.
In conclusion, tech-driven healthcare is revolutionizing the way we approach medical care, offering new opportunities to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and make healthcare more accessible. However, it is essential to address the challenges and ethical considerations that come with these advancements to ensure that the benefits of technology are realized by all. As we look to the future, the marriage of technology and healthcare promises to lead us into a new era of medical innovation, where the impossible becomes possible, and the future of healthcare is more personalized, efficient, and equitable than ever before.